ADSL-VDSL Technology  related subjects:
Digital modulation techniques,
Networking,
RF-electronics, TCP/IP
related subjects:
Digital modulation techniques,
Networking,
RF-electronics, TCP/IP |
| ADSL
a short introduction of Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) transmission
technology, ADSL
(Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) refers to a modulation scheme used to
deliver network traffic to a customer's residence using the same copper
twisted-pair wiring used for voice and ISDN service. It coexists with both
services, while offering 6-8Mbps speeds downstream and up to 640kbps upstream |
|
ADSL Basics (DMT) pdf file |
|
ADSL frequency spectrum Frequency allocation |
|
ADSL
modem - internet configuration the 4 variants or options that one has when
connecting a home or small office network to the Internet via an ADSL or Cable
modem |
|
ADSL Modem
simulation ADSL Modem simulation |
|
ADSL technology |
|
ADSL technology
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line, The main technologies used by the ADSL are:
Discrete MultiTone, Code & Error Correction, Framing & Scrambling, ... |
|
ADSL transmission applet
Java applets simulate here ADSL-like transmissions ... Basically ADSL uses
multiple carrier modulation : multiple QAM (Quadrature Amplitude modulation) |
|
ADSL
tutorial asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) is a new modem technology that converts existing twisted-pair telephone lines into access
paths for high-speed communications of various sorts |
|
ADSL2
tutorial Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL), a modem technology, converts existing twisted-pair telephone lines into access paths for
multimedia and high-speed data communications |
|
ADSL tutorial
ADSL transmits more than 6 Mbps to a subscriber, and as much as 640 kbps more in both directions |
| ADSL:
tutorial the essential concepts involved in making an ADSL connection to the internet,
pdf file |
| An introduction to DSL (Digital Subscriber Line),
xDSL, HDSL (High-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line), Single pair HDSL, SDSL,
ADSL |
|
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) Asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) is a new modem technology that converts existing twisted-pair telephone
lines into access paths for high-speed communications of various sorts |
|
Cable Technologies |
|
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) Digital Subscriber Line (DSL), Asymmetric
Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL), ADSL Technology, Very-High-Data-Rate Digital
Subscriber Line (VDSL) |
|
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line, ADSL Capabilities, ADSL Technology,
Signaling and Modulation, CAP and DMT Modulated ADSL, ADSL Standards and
Associations, Additional DSL Technologies, SDSL, HDSL, HDSL-2, G.SHDSL, ISDN
Digital Subscriber Line, VDSL |
|
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) pdf file |
|
Digital Subscriber
Lines and Cable Modems residential broadband networking, including ADSL,
HDSL, VDSL, RADSL, cable modems, pdf file |
|
DSL White Paper
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) is a broadband connection that uses the existing
telephone line, pdf file |
|
Setting up a wireless network
4 steps to set up your home wireless network, Choose your wireless equipment,
Connect your wireless router, Configure your wireless router, Connect your
computers |
|
The Splitter in
DSL Applications The Splitter in DSL Applications, pdf file |
|
Horizontaal |
VDSL Technology  related subjects:
Digital modulation techniques,
Networking,
RF-electronics, TCP/IP
related subjects:
Digital modulation techniques,
Networking,
RF-electronics, TCP/IP |
|
DSL Technology
Evolution ADSL2/ADSL2plus/ADSL-RE/VDSL2, pdf file |
|
ICT Regulation
Toolkit |
|
Standard VDSL Technology Overview of European (ETSI), North American
(T1E1.4) and International (ITU-T) VDSL standard development, pdf file |
|
Telecommunications Networks with VDSL2 VDSL2 (Very-High-Bit-Rate Digital
Subscriber Line 2), G.993.2, is the newest and most advanced standard of xDSL
broadband wireline communications. Designed to support the wide deployment of
Triple Play services such as voice, video, data, high definition television
(HDTV) and interactive gaming, VDSL2 enables operators and carriers to
gradually, flexibly, and cost efficiently upgrade existing xDSL-infrastructure,
... |
|
VDSL2 frequency spectrum doc file |
|
VDSL2 frequency spectrum
Telecommunications Networks with VDSL2 |
|
VDSL:
Introduction to VDSL System VDSL System allows fastest data transmission
among DSL technologies, pdf file |
|
VDSL2: taking the wire to the limit |
|
VDSL2 technology ADSL2plus is currently being deployed worldwide as the new
mainstream broadband technology for residential and business customers. But at
the same time, the industry is gearing up for the next step of the DSL
evolution: VDSL2. This second version of the very high-speed digital subscriber
line (VDSL) standard from ITU-T promises to deliver 100Mbps symmetrical traffic
on short copper loops, VDSL: Very High Speed Digital Subscriber Line, pdf file |
|
VDSL2
white paper |
|
Very-High-Data-Rate Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) VDSL is the highest-rate DSL technology available. Running at speeds of up to 52 Mbps, VDSL is the next
generation of DSL, with higher throughput and simpler implementation
requirements than ADSL, pdf file |
|
Very-High-Data-Rate Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) pdf file |
VDSL2- Next important broadband technology ADSL2plus is currently being
deployed worldwide as the new mainstream broadband technology for residential
and business customers. But at the same time, the industry is gearing up for the
next step of the DSL evolution:
VDSL2, pdf file |
|
The Splitter in
DSL Applications The Splitter in DSL Applications, pdf file |
|
Horizontaal |
|
|
ADSL frequency spectrum: |
|
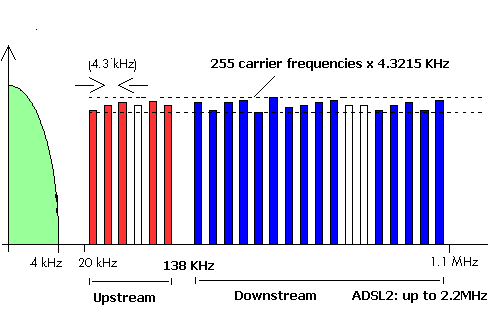 |
|
|
VDSL frequency spectrum (up to 30MHz): |
|
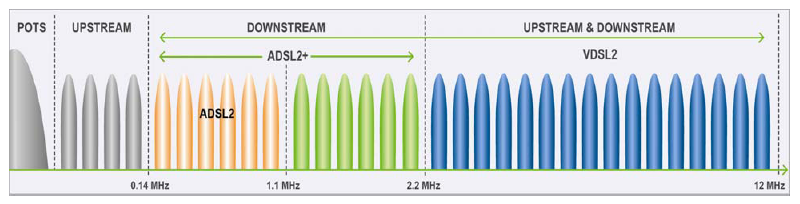 |
|
|
|
|
xDSL Comparison table: |
|
Technology |
Upstream capacity |
Downstream capacity |
Maximum distance |
BW |
Tone spacing |
Type |
Standard |
|
ADSL |
640 Kb/s |
8 Mb/s |
6 km |
1.104 MHz |
4.3125 KHz |
asymmetric |
G.992.1 |
|
ADSL2 |
1 Mb/s |
12 Mb/s |
3 km |
1.104 MHz |
4.3125 KHz |
asymmetric |
G.992.3 |
|
ADSL 2+ |
1 Mb/s |
24 Mb/s |
4.3 km |
2.208 MHz |
4.3125 KHz |
asymmetric |
G.992.5 |
|
VDSL |
15 Mb/s |
55 Mb/s |
1.3 km |
12 MHz |
4.3125 KHz |
asymmetric
or symmetric |
G.993.1 |
|
VDSL 2 |
100 Mb/s |
100 Mb/s |
0.6 km |
30 MHz |
8.625 KHz |
asymmetric
or symmetric |
G.993.2 |
Remarks:
- xDSL means all type of DSL
- symmetric: downstream and upstream rates are the same.
- asymmetric: downstream rate is higher than the upstream rate
- VDSL2 BW bandplan configuration options: 8.5, 12, 17.7 and 30 MHz
- VDSL2 30 MHz bandplan: Upload: 25-138 KHz, 3.75-5.2 MHz, 8.5-21.567 MHz;
Download: 138 KHz-3.75 MHz, 5.2-8.5 MHz, 21.567-30 MHz
|
|
|
Home
|
Site Map
|
Email: support[at]karadimov.info
Last updated on:
2011-01-02
|
Copyright © 2011-2021 Educypedia.
http://educypedia.karadimov.info
|
| |