Acoustics and Sound Technology topics  related topic: Decibels,
Speech -anatomy
related topic: Decibels,
Speech -anatomy |
|
Absorption coefficients and impedance Absorption coefficients and impedance |
|
Acoustic high-pass, low-pass, and band-stop filters Acoustic high-pass,
low-pass, and band-stop filters |
| Acoustic echo suppression
animated, in vehicle acoustic echo reduction using complementary comb filters |
|
Acoustic impedance sound travels through materials under the influence of sound pressure. Because molecules or atoms of a solid are bound elastically to
one another, the excess pressure results in a wave propagating through the solid. The acoustic impedance (Z) of a material is defined as the
product of density (p) and acoustic velocity (V) of that material |
| Acoustic impedance
What is acoustic impedance and why is it important? |
| Acoustic material property tables
solids, longitidunal piezoelectric, shear piezoelectric, plastics, rubbers,
liquids, gases |
|
Applying
Harmonics |
|
Auditory scales of frequency representation pitch, frequency, bandwidth |
|
Beat frequency two sound waves of different frequency, what is Beat
frequency, beat frequencies, or difference tones, result when two frequencies
which are very close in frequency occur simultaneously |
| Beats
when two harmonically-related sine waves (sinusoids) are added together, the two distinct tones tend to fuse
together in our auditory system to produce a sensation of a single pitch. Additionally, the timbre of the resultant tone is associated with the
resultant waveform |
| Beats
what are Beats |
|
Beats
When two sound waves of different frequency approach your ear, the alternating
constructive and destructive interference causes the sound to be alternatively
soft and loud - a phenomenon which is called "beating" or producing beats, ... |
|
Beats
rapid changes in loudness, known as beats, occur when two tones very close in
frequency are heard at the same time. The number of beats is equal to the
difference in two nearly similar frequencies |
|
Beats |
|
Capacité dynamique est la capacité d'un systéme audio à reproduire un son à un niveau réaliste,
en Français |
|
Characteristics of Sound and the Decibel Scale |
|
Classroom acoustics |
|
Decibel
Acoustics / Noise,
dB, dBf, dBK, dBm, dBu, dBV, dBW, What is a
decibel? the decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit used to describe a ratio.
The ratio may be power, or voltage or intensity or several other things,
filters used for dBA and dBC, typical average decibel levels of some common
sounds |
|
Decibel
(Loudness) Comparison Chart |
|
Decibels
Definition and examples, Sound files to show the size of a decibel, Standard
reference levels, absolute sound level, Logarithmic response, psychophysical
measures, sones and phons, Recording level and decibels (dBV and dBm),
Intensity, radiation and dB, dBi and anisotropic radiation, Example problems
using dB for amplifier gain, speaker power, hearing sensitivity, What is a
logarithm? |
|
Decibels Definition and Logarithmic Calculation |
|
Equal-loudness
contour An equal-loudness contour is a measure of sound pressure (dB SPL),
over the frequency spectrum, for which a listener perceives a constant loudness.
The unit of measurement for loudness levels is the phon, and by definition two
sine waves that have equal phons are equally loud, ... |
| Equal
loudness curves what are Equal loudness curves |
| Equal loudness tester
this site allows you to measure equal loudness curves, the frequency response of your own ears. The flash script allows you to play sound files with a range of
frequencies and sound levels with the click of a mouse |
| Fletcher-Munson curve explanation loudness curves
(Fletcher-Munson curves) |
|
Fletcher-Munson equal-loudness contours Equal loudness contours or
Fletcher-Munson curves |
| Fourier approximations and music
introduces Fourier approximations of periodic functions in the context of
musical sounds |
| Frequency spectrum of a sound a sound which consists of a single frequency is called a pure tone, musical sounds contain a fundamental frequency plus
several harmonics |
|
Geluidshinder
pdf file, in Dutch |
| Hydrophones
hydrophones, what are
hydrophones |
|
Introduction to Harmonics pdf file |
|
Larsen effect
What is Acoustic Feedback, what is Larsen effect,
pdf file |
|
Larsen effect
The Larsen effect, better known as the electroacoustic phenomenon of feedback
between microphone and amplifier |
|
Larsen effect
Audio feedback (also known as the Larsen effect) is a special kind of feedback
which occurs when a loop exists between an audio input (for example, a
microphone or guitar pickup) and an audio output (for example, a loudspeaker),
... |
|
Loudness loudness is a subjective term describing the strength of the ear's perception of a sound. It is intimately related to sound intensity but can by no
means be considered identical to intensity |
|
Loudness
loudness |
| Nine components of sound
components of sound: music components: pitch, timbre, harmonics, loudness, rhythm, attack, sustain, decay, speed |
|
Phonetics
Phonetics is the study of the articulatory and acoustic properties of the sounds
of human language |
|
Phons
the loudness of complex sounds can be measured by comparison to 1000Hz test tone |
|
Pitch (music)
In music, pitch is the psychological correlate of the fundamental frequency of a
note, ... |
|
Pitch Pitch = frequency of sound, For example, middle C in equal temperament
= 261.6 Hz |
|
Pressure Amplitude:
Quantitative Measurement of Sound |
|
Seeing
with your ears java demonstration of an auditory display for vision substitution. Includes image sonification and spectrogram generation |
|
Sensation and perception
Waveforms and Frequency Analysis, Why does the auditory system analyse sound by
frequency? Sine waves, Complex periodic sounds, Linearity, Filters, Resonance,
Response to single pure tones, Frequency threshold curves, Characteristic
frequency, Phase locking, Coding frequency, Coding intensity, Two-tone
suppression, ... |
|
Sone what are
sones |
| Sones
a unit of loudness, what are sones |
|
Sound
Effects Expansion/Noise Gating, Equalization, Compression/Limiting, Phase
Shifting (Phasing), Ring Modulation, Chorus, Delay, Reverberation, Flanging |
|
Sound examples
sound examples, a tip |
|
SOUND
FILES |
|
Sound
levels Sound Pressure, Sound Pressure Level, Weighted Sound Level, Fletcher
and Munson Contours |
|
Sound Pressure Level
Sound pressure level is a measurement of the pressure of a sound in relation to
a fixed reference point, ... |
|
Sound Pressure Level Sound Pressure Level, SPL, What is SPL |
|
Sound Pressure Level
Sound Pressure Level, SPL, What is SPL, Sound pressure level (SPL) or sound
level Lp is a logarithmic measure of the rms pressure (force/area) of a
particular noise relative to a reference noise source |
|
Sound Pressure Level
chart Sound Pressure Level chart, pdf file |
| Sound spectrum
sound spectrum is a representation of a sound - usually a short sample of a sound - in terms of the amount of vibration at each individual
frequency. It is usually presented as a graph of either power or pressure as a function of frequency. The power or pressure is measured in decibels and the
frequency is measured in vibrations per second (or Hertz, abbreviation Hz) or thousands of vibrations per second (kiloHertz, abbreviation kHz) |
|
Sound Transmission Sound Transmission, sound propagation, Decibels measured
in intensity or pressure, Interference, pdf file |
|
Sound waves sound waves |
|
Sound waves sound waves,
Speed of sound in various media, Displacement and pressure variations in sound
waves, Interference, Constructive and destructive interference of sound waves,
Intensity, Sound intensity and decibel levels, Doppler Effect applied to sound |
|
Sound Waves and Music |
|
Spectrograms What are spectrograms,
What are waveforms? What are spectrograms? What are phonemes? What are formants |
| The physics of music
Measurement and Units, The Simple Harmonic Oscillator, Waves, Structure of the
ear, Loudness and Decibels, Standing Waves, Pure and complex tones, Ohm's Law of
Hearing, Time, Frequency and spectrum, Musical Intervals and Scales,
"Scientific" theory of consonance, Room Acoustics |
|
Timbre |
|
Timbre In
music, timbre, also timber (from Fr. timbre), is the quality of a musical note
or sound that distinguishes different types of sound production or musical
instruments |
| Timing errors and jitter a discussion of the various types of
jitter, their causes and effects on converter performance, pdf file |
| Ultra
sonic testing a tip |
| Velocity of the
sound waves sound waves travel at different velocities depending upon the
physical properties of the medium through which they are travelling |
| Vocal tract
acoustics speech, acoustics, vocal tract, helium speech, helium, acoustic impedance, sound spectrum, decibel |
|
Waves |
|
Waves, acoustics and vibrations Diffraction, Waves in Three Dimensions, The
Auditory Sense, Vibrations of Air Columns, Vibrations of Stretched Strings,
Theory of the String Telegraph, Vibrations of Flat Things, Waves in Solids,
Surface Waves on Liquids, Musical Scales |
|
Waves in strings, reflections, standing waves and harmonics waves in strings, reflections, standing waves and harmonics |
|
What is noise? |
|
Horizontaal |
|
|
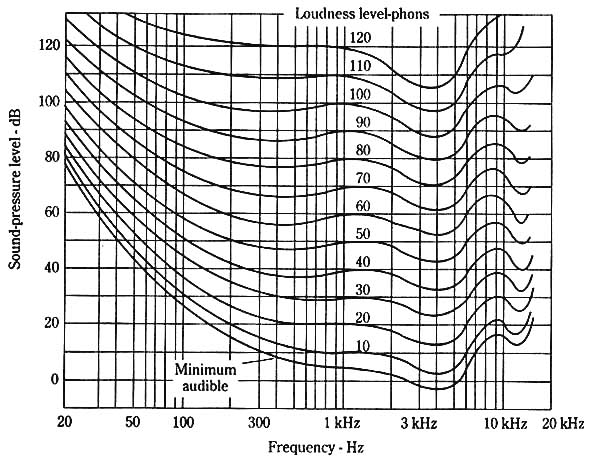
Sound Pressure level Chart: |
|
 |
|
|
About
|
Site Map
|
Email: support[at]karadimov.info
Last updated on:
2011-01-02
|
Copyright © 2011-2021 Educypedia.
http://educypedia.karadimov.info
|