| Analog radio:
general overview related subject: PLL |
|
Amplitude Modulated Radio Frequency Transmission System Receiver and
Demodulator,
pdf file |
|
Electronic and radio theory
radio receiver basics, crystal radio set, tuned radio frequency TRF variety, superheterodyne receiver |
|
Explore inside of a
radio investigates the inside of a cheap beach radio |
| FM radiostations in Belgium |
|
FM Stereo Radio MPX with RDS |
|
FM Stereo Radio MPX with RDS pdf file |
| Frequency devices
design guide, solving real world signal conditioning problems |
|
How radio works explore the technology of radio |
| Radio calculator
scientific calculator and universal converter for radio communication, a tip |
|
Radio
receiver tuning, frequency conversion, modulation, demodulation |
| Radio receiver handbook radio receivers, from crystal set to
stereo, Radio Receiver, The Antenna, The Ground, Radio Receiver with TDA7050 IC,
Radio Receiver with LM386 IC, Radio Receiver with Increased Sensitivity Audio
Amplifier, Universal Audio Amplifier, Receiver with HF Amplifier, Direct
Receiver with Drain Detector, Direct SW Receiver for AM, AM-SSB & CW Signals,
Miniature Receiver with ZN414 (ZN414Z) IC, Direct (TRF) FM Receivers, FM
Receiver with Audio Amplifier, FM Receiver with One Transistor and Audio
Amplifier, a tip |
| Radio receiver technology
Radio receiver technology, measurement techniques, radio propagation, radio and
electronics history, amateur radio |
|
RDS/EON Car Radio System a computer controlled high-end AM/FM car radio
system with RDS/RBDS decoding. It is based on a single 8051 family
microcontroller (P83CE528) and various I2C-bus controlled peripherals |
|
Receivers 1Many receivers must be capable of handling a very wide range of
signal powers at the input while still producing the correct output. This must
be done in the presence of noise and interference which occasionally can be much
stronger than the desired signal,
pdf file |
| RF
tutorials for EEs mixers, RF directional couplers, impedance transformers |
|
Single-Chip
PLL-FM-Receiver Single Superheterodyne PLL-FM-Receiver, Low Noise Amplifier
(LNA), Input Impedance Matching & Noise, Considerations, Input matching,
Filtering, Implementation, LNA Core, Input and Output filters, Mixer,
Implementation, Local Oscillator, Oscillator, Tuning, Buffers, PLL Frequency
Synthesizer, Crystal Oscillator (XO), Intermediate Frequency Amplifier, IF
Amplifier Design, FM Demodulator Design, Phase Shift Network, LNA, Mixer, Local
Oscillator, PLL, Xtal Oscillator, IF Amplifier, Phase Shift Network, Demodulator Demodulator Output |
|
TEA
6848H TEA 6848H is for small dimensioned Electronic Tuned AM/FM Car Radio
receiver, with advantage in application-area’s where the FM band is crowded,
pdf file |
| Time and frequency
articles frequency synthesis and conversion, Phase Noise/ AM noise, oscillator circuits, power supply circuits, RF amplifier circuits, shock and
vibration |
|
VHF community radio electronics the concepts involved in
radio broadcasting relevant to the community radio operator on VHF FM, a typical
VHF FM transmitter system |
| Williamson labs
communications, computers, antennas, data sheets, decoupling, electronic design automation, electromagnetic compatibility, radio, amplifiers, inductors, operational amplifiers, op amps, optics, oscillators, oscilloscopes, rf, modulation, heterodyne, mixer, double sideband, dsb, single sideband, ssb, amplitude modulation, am, frequency modulation, fm, shielding, sound, piezo, seebeck, peltier, video, vga, vcr, raster, tv, television, ntsc, pal, rs-170, rs-170a, bipolar transistors, bjt, field effect transistors, fet, mosfet,
a tip |
|
Horizontaal |
Analog radio: topics
 related subject:
Crystal radio circuits,
PLL, RF circuits related subject:
Crystal radio circuits,
PLL, RF circuits |
|
AM-FM
Ceramics 450 - 470 kHz AM Filters, 10.3 - 11.5 MHz FM Filters |
|
AM radio receiver
pdf file |
|
AM
radio receivers How AM radio receivers work, An AM Radio Realized with
Only Discrete Bipolar Transistors, pdf file |
|
AM
SUPERHETERODYNE RECEIVERS IF section, AM receivers, diode detector |
|
AM transmitters and receivers
AM communication, AM transmitters and receivers, pdf file |
|
AM transmitters and receivers
AM communication, AM transmitters and receivers, pdf file |
|
AM/FM car radio receivers
How AM radio receivers work, How FM radio receivers work, IF
amplifier/demodulator for FM car radio receivers, AM/FM radio receiver circuit,
Front-end and PLL synthesizers for car radios |
| Ceramic
filters and resonators How Ceramic filters and resonators work |
|
COILS AND TRANSFORMERS Coils, Transformers, Working principles and
characteristics of transformers |
|
Conversion
gain and noise temperature heterodyne mixer, hetrodyne receiver |
|
Crystal oscillators
How Crystal oscillators work |
|
Crystal radio
optimal loading of audio transformers for crystal set use |
|
Crystal radio
crystal radio, how the
crystal radio work |
|
Crystal radio plans,
Cristadyne links |
|
Crystal
receivers crystal receiver history, crystal receiver construction projects |
|
Crystal
set |
|
Crystal technology |
|
Demodulation of AM signals
envelope detector,
pdf file |
|
Demodulation of AM signals
Demodulation of AM signals, Notes on the Demodulation of AM Signals,
pdf file |
|
Demodulation of AM signals
Demodulation of AM signals, The DSBSC modulation is one type of modulation in
which the information (or message) is carried on the amplitude of a sinusoidal
signal. Another type of this modulation is what we can call Double Side Band
Including Carrier or Full AM (or simply AM), doc file |
|
Envelope detector how the
envelope detector work |
|
Envelope detector
envelope detector, how the
envelope detector work |
| Feedback
oscillators and lasers phase shift oscillator, RC oscillator, optical
oscillator |
|
FM
demodulation FM
demodulation, Quadratur demodulator,
Foster-Seeley discriminator,
pdf file |
| FM
demodulation FM
demodulation, Quadratur demodulator, Foster-Seeley discriminator |
|
FM Detectors
(Discriminators) FM detectors convert the frequency variations of the
carrier back into a replica of the original modulating signal. There are 5 basic
types of FM detectors: Slope detector, Foster-Seely Discriminator, Ratio
Detector, Quadrature Detector, Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) detector |
| FM radio
receivers FM radio
receivers, FM communication techniques |
|
FM receiver FM Receiver with one Transistor and Audio Amplifier |
|
FM
receivers FM receivers, FM communication techniques |
|
FM stereo FM stereo signal, RDS, FM communication techniques, Radio Data System |
|
FM stereo
how FM stereo work |
|
FM stereo
FM modulation used in the 87.5MHz to 108MHz band takes a signal with frequency range
~50Hz to ~15kHz and modulates a carrier in the FM band with a modulation index
of ~5 |
|
FM-Stereo-RDS Modulation
FM theory, FM stereo multiplexing and the RDS
mechanism, Frequency modulation (FM) has a long history of its application and
is widely used in radio broadcast. To transmit stereo music, FM is enhanced by
stereo multiplexing which carries both L and R audio channel content. With the
digital age, Radio Data System (RDS) enables FM to carry text information such
as traffic, weather, and radio station information which can be displayed on the
end-user’s device interface, pdf file |
|
FM Stereo Tuner
Measurement Pilot, Stereo Subcarrier suppressed, RDS Subcarrier, pdf file |
|
Heterodyne Principle generate new frequencies by mixing two or more signals
in a nonlinear device such as diode mixer |
| IF
transformer |
|
LC AM radio
construct a simple AM receiver using a "Tank" circuit and a Envelope Detector
circuit |
|
LC filter design learn the basics of LC filter design, pdf file |
|
LM3189 FM IF System The LM3189N is a monolithic integrated circuit that
provides all the functions of a comprehensive FM IF system. The block diagram of
the LM3189N includes a three stage FM IF amplifier/limiter configuration with
level detectors for each stage, a doubly balanced quadrature FM detector and an audio amplifier that
features the optional use of a muting (squelch) circuit, pdf file |
|
Mathematical analysis of
frequency mixing Mathematical analysis of frequency mixing, describing the
mixing of two frequencies in a non-linear circuit |
|
Mixer design
describing the mixing of two frequencies in a non-linear circuit, Mixer spectral
output,
pdf file |
|
Mixers |
| Mixers:
a introduction a mixer converts RF power at one frequency into power at another
frequency to make signal processing easier and also inexpensive |
|
Mixers and frequency conversion mixers and frequency conversion |
|
Mixers,
diode the use of mixers and heterodyne receivers to detect and process RF
signals |
| Mixers in
communications
the linear diode detector for AM demodulation, product detector for SSB, DSB,
and CW demodulation, quadrature demodulator, BPSK signal, QPSK signal, filter
method of SSB generation, phasing method of SSB generation |
| Mixing and modulation
techniques animated, a tip |
| Negative
resistance oscillators Gunn oscillators, Negative Resistance, Gunn effect, Negative resistance oscillator |
|
Oscillator design
pdf file |
|
Oscillator design
pdf file |
|
Phase-Locked Loop |
|
Preemphasis
and deemphasis in an FM system the higher frequencies contribute more to the
noise than the lower frequencies. Because of this all FM systems adopt a system
of preemphasis where the higher frequencies are increased in amplitude before
being used to modulate the carrier |
| Quad
detector a quadrature detector is used to demodulate frequency shift
keying (FSK) and other types of FM signals |
| Quadrature FM
detectors FM stands for Frequency Modulation. It means that the
RF-frequency will change acording to the input audio signal |
|
Ratio detector
The RF input V0 is applied to the coil L0. The capacitor C0 is not very
essential for understanding the principle of the ratio detector. Its value is
selected so that L0-C0 tank circuit resonates at the center frequency of FM
modulation of the RF input, in order to cancel the inductance of the detector
seen from the RF signal source |
|
Ratio detector |
|
Ratio detector |
|
Receivers Detection of AM, FM, and SSB, AM Detector, AGC,
ppt file |
|
Receptiion of Amplittude Modulated Siignals AM Demodulation The purpose of
this experiment is to show how the amplitude-modulated signals are demodulated
to obtain the original signal,
pdf file |
|
Regenerative receivers the use of feedback in the reflex receiver allowed a single
transistor to be used simultaneously as an amplifier for both RF and AF
signals |
|
Superheterodyne Radio Receivers Superheterodyne Radio Receivers,
Superheterodyne AM Receivers, The Simplest Superheterodyne AM Receiver |
|
Superheterodyne Receivers
pdf file |
|
Superheterodyne receivers Spurious responses of mixers,
pdf file |
|
Superheterodyne receiver |
|
Superheterodyne receiver
Superheterodyne receiver |
|
Synthesiser design a
synthesiser is a device which takes an input, or source, frequency and from it
produces an output frequency which is either directly or indirectly related to
it,
pdf file |
|
TDA1597 IF amplifier/demodulator
The TDA1597 provides IF amplification, symmetrical quadrature demodulation and
level detection for quality home and car FM radio receivers and is suitable for
mono and stereo reception. It may also be applied to common front-ends, stereo
decoders and AM receivers circuits |
|
Varactor tuner |
|
Wide
band RF transformers wideband RF transformers are simply transfomers
designed to provide an impedance transformation over a broad frequency range.
In amateur radio applications we wind these transformers on ferrite toroids. A
common impedance transformation is 200 ohms to 50 ohms using a bi-filar
winding, pdf file |
|
Horizontaal |
|
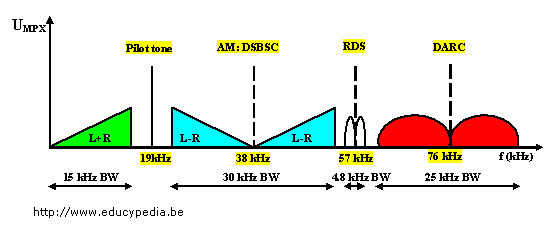
Composite FM signal with RDS and DARC |
Audio : 30 Hz – 15 kHz
Subcarriers: 38 kHz, 57 kHz, 76 kHz, suppressed
Pilot tone: 19 khz
RDS: BW: 54.625 – 59.375 kHz
DARC: DARC (DAta Radio Channel), an FM multiplex broadcast technology, LMSK
(Level Minimum Shift Keying) subcarrier; BW: 60 – 95 kHz
|
|
 |
|
|
Home
|
Site Map
|
Email: support[at]karadimov.info
Last updated on:
2011-01-18
|
Copyright © 2011-2021 Educypedia.
http://educypedia.karadimov.info
|
| |