Transmission
lines  related subject: Antennas, Cabling theory,
Electro magnetic waves,
RF transformers,
TDR Measurements,
Waves (physics)
related subject: Antennas, Cabling theory,
Electro magnetic waves,
RF transformers,
TDR Measurements,
Waves (physics) |
| Ligne de transmission
en Français, pdf-file |
| Antennas
& Transmission Lines cables and waveguides, pdf-file |
|
Transmission lines
finite resistance in transmission lines, proximity effect in transmission lines, a physical phenomenon that
cause opposing currents in adjacent wires to draw toward one another, the
proximity effect is caused by changing magnetic fields and therefore does
not occur for low frequency signals, a tip |
|
Transmission line
and termination Characteristic impedance of a coax cable and twin lead
cable, balun, twisted pair, impedance matching, ppt
file |
|
Transmission lines pdf-file |
|
Transmission lines pdf-file |
|
Transmission lines
The transmitter that generates the RF power to drive the antenna is usually
located at some distance from the antenna terminals. The connecting link between
the two is the RF transmission line. Its purpose is to carry RF power from one
place to another, and to do this as efficiently as possible,
pdf-file |
| Transmission lines
a tip, animated |
|
Transmission
lines pdf-file |
|
Transmission lines ppt file |
|
Transmission lines ppt file |
|
Transmission lines |
| Transmission lines
definitions for transmission lines, microwaves, power flow on transmission
lines, stub tuner matching, the SMITH chart, standing wave patterns, microwave
measurements, scattering parameters and the S-matrix, waveguides and cavity
resonators, microstrip |
| Transmission
lines and antennas wave propagation, sound waves, light waves, electric field, speed of light, polarization, sky wave, ionosphere, refraction,
transmission lines, tropospheric, reflection, terminating, standing waves, characteristic impedance, radiations, folded dipole, radiation resistance |
| Transmission
lines and antennas electromagnetic fields and waves, cable, coax cable,
twin |
| Transmission line
transformers balun, Guanella 1:4 balun |
|
Transmission line transformers pdf-file |
|
Transmission lines tutorial explores transmission line behavior,
educypedia |
| Transmission
lines tutorials transmission line tutorials in pdf format,
a tip |
| Transmission
line impedances |
|
Transmission lines
properties Balance-to-ground, unbalanced transmission line, balanced
transmission line, characteristic impedance, parallel conductor line,
coaxial cable, Attenuation per unit length, Skin effect, attenuation per
unit length, wave propagation velocity, electrical length |
| Transmission line theory pdf-file |
|
Transmission sur lignes en Français, pdf
file |
|
Understanding Coaxial RF Transmission Lines by Measurement and Calculation
Page 1 |
|
Horizontaal |
|
|
Characteristic impedance calculation:
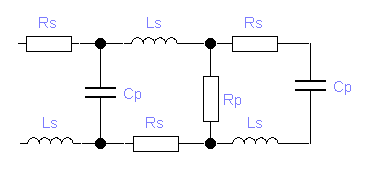
|
| Twincable (300
W ) |
Coax cable (50, 75, ..
Ohm ) |
-
L = 2.7 µH/m
-
C = 30 pF/m
-
Rs = 0.15
W/m
-
Rp = 1014
W/m
|
-
L = 0.5 µH/m
-
C = 47 pF/m
-
Rs = 0.002
W/m
-
Rp = 1012
W/m
|
|
|
|
|
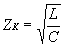
Coax cable:
|
Zk = 138/√er
. log(D/d) (W)
L = µrµ0/2p
. ln(D/d) (H/m)
C = 2pere0/
ln(D/d) (F/m) |
er:
dielectric constant
(relative permittivity) of the medium (if you don't know take 2.3,
Polyethylene), air = 1
e0: permittivity of free
space: 8.8542.10-12 F/m
d : the diameter of the inner conductor
D : the diameter of the outer conductor
µ0: Permeability of a vacuum: 4xp×10-7 H/m
µr:
relative permeability of the medium: air = 1
Twin lead (balanced pair):
|
Zk = 276/√er
. log(2a/d) (W)
L = µrµ0/p
. ln(2a/d) (H/m)
C = pere0/
ln(2a/d) (F/m) |
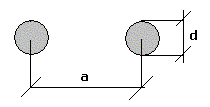
µr: relative permeability of the medium |
|
Horizontaal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Home
|
Site Map
|
Email: support[at]karadimov.info
Last updated on:
2011-01-02
|
Copyright © 2011-2021 Educypedia.
http://educypedia.karadimov.info
|
| |